Phi Silica용 LoRA 미세 조정
Low Rank Adaptation(LoRA)을 사용하여 Phi Silica 모델을 특정 사용 사례에 맞게 성능을 향상시키도록 미세 조정할 수 있습니다. LoRA를 사용하여 Microsoft Windows 로컬 언어 모델인 Phi Silica를 최적화하면 더 정확한 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다. 이 프로세스에는 LoRA 어댑터 학습 후 추론 시 적용하여 모델 정확도를 향상시키는 과정이 포함됩니다.
Phi Silica 기능은 중국에서 사용할 수 없습니다.
전제 조건
- Phi Silica의 응답을 향상시키기 위한 사용 사례를 식별했습니다.
- '좋은 응답'을 결정하기 위한 평가 기준을 선택했습니다.
- Phi Silica API를 사용해 보았지만 평가 기준을 충족하지 못했습니다.
어댑터 학습
Windows 11에서 Phi Silica 모델을 미세 조정하기 위한 LoRA 어댑터를 학습하려면 먼저 학습 프로세스에서 사용할 데이터 세트를 생성해야 합니다.
LoRA 어댑터에 사용할 데이터 세트 생성
데이터 세트를 생성하려면 데이터를 두 개의 파일로 분할해야 합니다.
train.json: 어댑터 학습에 사용됩니다.test.json: 학습 중 및 학습 후 어댑터 성능 평가에 사용됩니다.
두 파일 모두 JSON 형식을 사용해야 하며, 각 줄은 단일 샘플을 나타내는 별도의 JSON 객체입니다. 각 샘플에는 사용자 및 어시스턴트 간에 교환된 메시지 목록이 포함되어야 합니다.
모든 메시지 객체에는 두 개의 필드가 필요합니다.
content: 메시지의 텍스트입니다.role: 발신자를 나타내는"user"또는"assistant"입니다.
다음 예제를 참조하세요.
{"messages": [{"content": "Hello, how do I reset my password?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "To reset your password, go to the settings page and click 'Reset Password'.", "role": "assistant"}]}
{"messages": [{"content": "Can you help me find nearby restaurants?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "Sure! Here are some restaurants near your location: ...", "role": "assistant"}]}
{"messages": [{"content": "What is the weather like today?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "Today's forecast is sunny with a high of 25°C.", "role": "assistant"}]}
학습 팁
- 각 샘플 줄 끝에 쉼표를 넣을 필요는 없습니다.
- 가능한 한 많은 고품질의 다양한 예제를 포함하세요. 최상의 결과를 얻으려면
train.json파일에 최소 몇천 개의 학습 샘플을 수집하세요. test.json파일은 더 작을 수 있지만 모델이 처리해야 할 것으로 예상되는 상호 작용 유형을 포함해야 합니다.- 각 줄에 하나의 JSON 객체가 포함된
train.json및test.json파일을 만듭니다. 각 객체에는 사용자 및 어시스턴트 간의 간략한 대화가 포함됩니다. 데이터의 품질과 양은 LoRA 어댑터의 효과에 크게 영향을 미칩니다.
LoRA 어댑터 학습
LoRA 어댑터를 학습하려면 다음 필수 구성 요소가 필요합니다.
- Azure 구독 및 Azure Container Apps의 사용 가능한 할당량.
- 미세 조정 작업을 효율적으로 실행하려면 A100 GPU 이상을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
- Azure Portal에서 사용 가능한 할당량을 확인하세요. 할당량 찾기에 대한 도움이 필요하면 할당량 보기를 참조하세요.
다음 단계에 따라 작업 영역을 만들고 미세 조정 작업을 시작하세요.
-
모델 도구 > 미세 조정으로 이동하여 새 프로젝트를 선택합니다.
-
모델 카탈로그에서 "microsoft/phi-silica"를 선택하고 다음을 선택합니다.
-
대화 상자에서 프로젝트 폴더를 선택하고 프로젝트 이름을 입력합니다. 프로젝트에 대한 새 VS Code 창이 열립니다.
-
방법 목록에서 "LoRA"를 선택합니다.
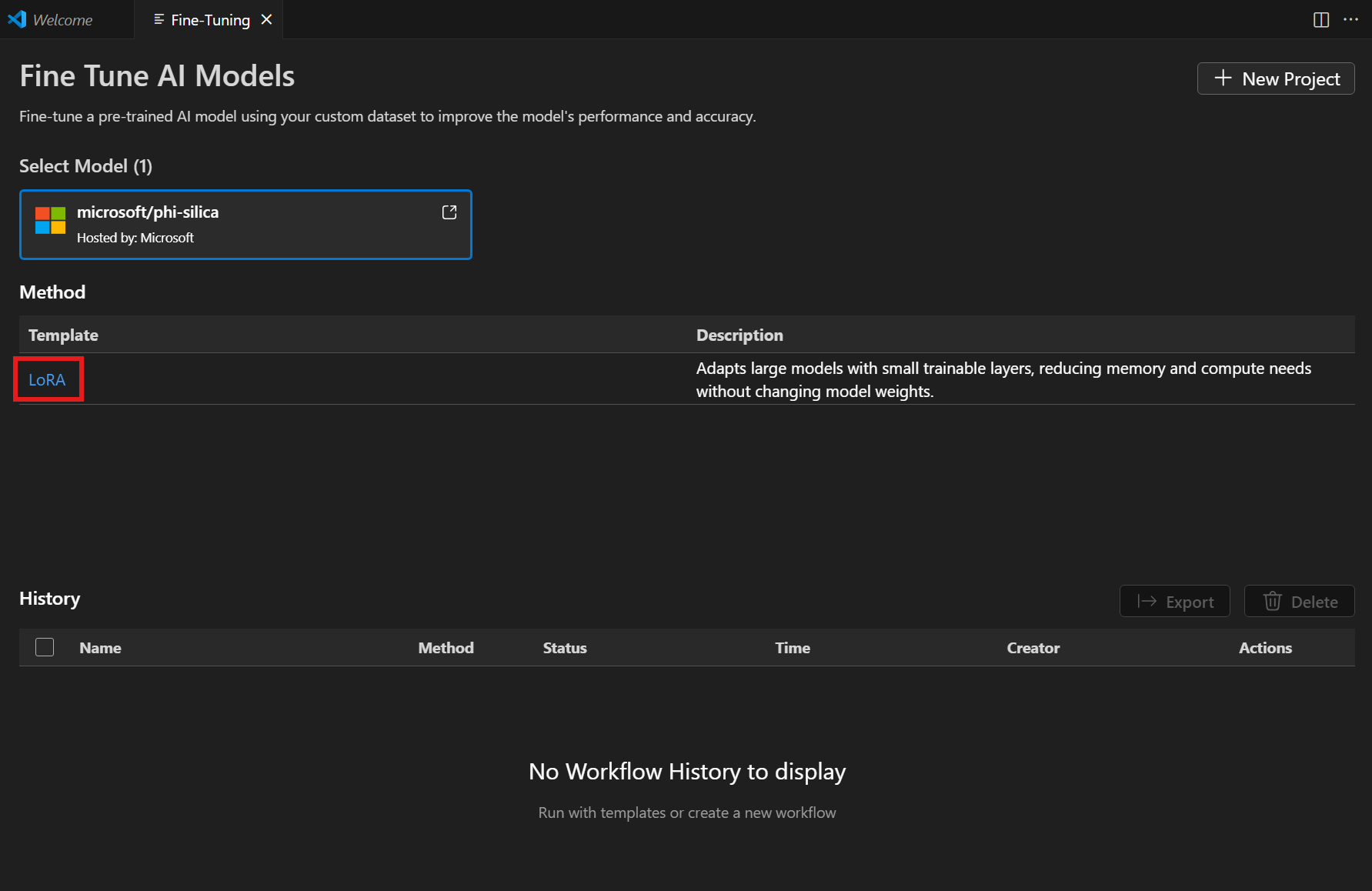
-
데이터 > 학습 데이터 세트 이름 및 테스트 데이터 세트 이름 아래에서
train.json및test.json파일을 선택합니다. -
클라우드에서 실행을 선택합니다.
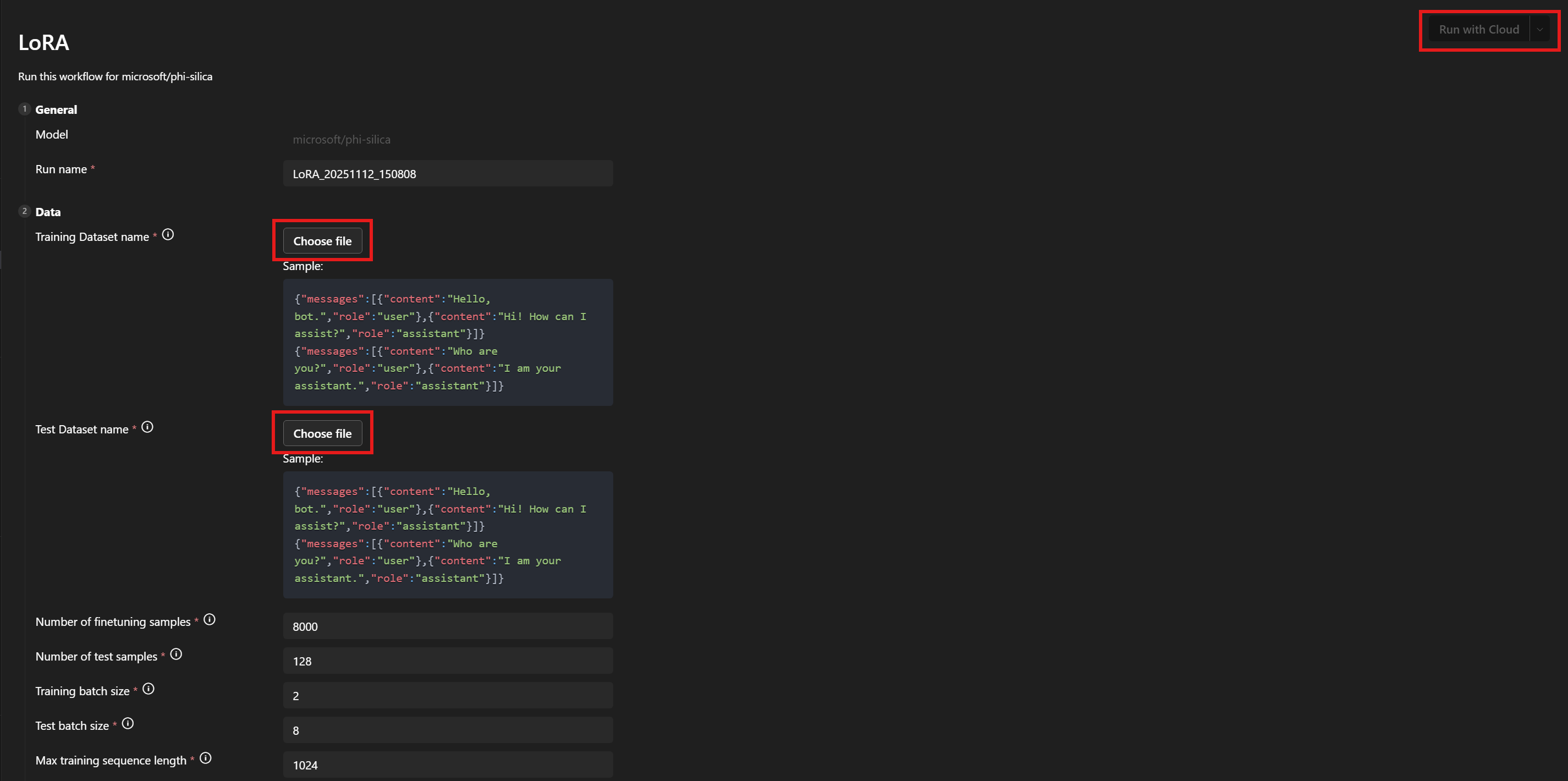
-
대화 상자에서 Azure 구독에 액세스하는 데 사용할 Microsoft 계정을 선택합니다.
-
계정이 선택되면 구독 드롭다운 메뉴에서 리소스 그룹을 선택합니다.
-
미세 조정 작업이 성공적으로 시작되고 작업 상태가 표시됩니다.
새로고침 버튼을 사용하여 상태를 수동으로 업데이트하세요. 미세 조정 작업이 완료되는 데 일반적으로 평균 45~60분이 걸립니다.
-
작업이 완료되면 다운로드를 선택하여 새로 학습된 LoRA 어댑터를 다운로드하고 지표 보기를 선택하여 미세 조정 지표를 확인할 수 있습니다.
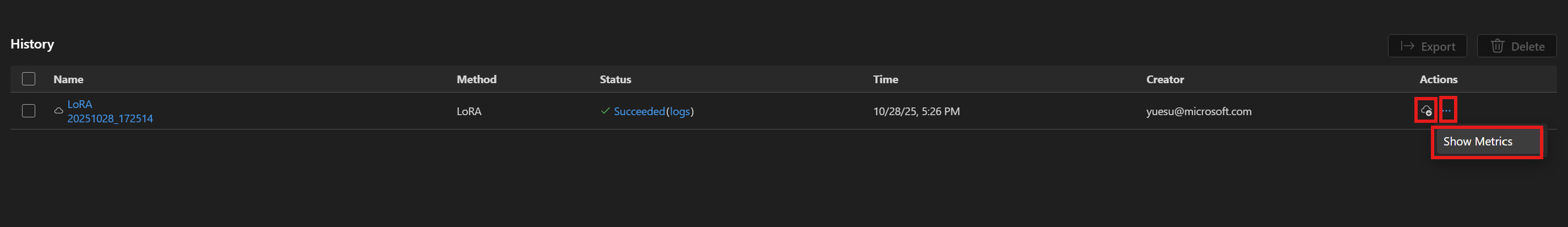
LoRA 미세 조정 권장 사항
하이퍼파라미터 선택
LoRA 미세 조정을 위해 설정된 기본 하이퍼파라미터는 비교를 위한 합리적인 기준 미세 조정을 제공해야 합니다. 대부분의 사용 사례 및 데이터 세트에 잘 맞는 기본값을 찾기 위해 최선을 다했습니다.
하지만 원하는 경우 매개변수 검색을 위한 유연성을 남겨두었습니다.
학습 하이퍼파라미터
표준 매개변수 검색 공간은 다음과 같습니다.
| 매개변수 이름 | 최소 | 최대 | 분포 |
|---|---|---|---|
| learning_rate | 1e-4 | 1e-2 | 로그 균일 |
| weight_decay | 1e-5 | 1e-1 | 로그 균일 |
| adam_beta1 | 0.9 | 0.99 | 균일 |
| adam_beta2 | 0.9 | 0.999 | 균일 |
| adam_epsilon | 1e-9 | 1e-6 | 로그 균일 |
| num_warmup_steps | 0 | 10000 | 균일 |
| lora_dropout | 0 | 0.5 | 균일 |
또한 linear_with_warmup 또는 cosine_with_warmup 중 하나를 선택하는 학습률 스케줄러를 검색합니다. num_warmup_steps 매개변수가 0으로 설정된 경우 선형 또는 코사인 옵션을 동등하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
학습률, 학습률 스케줄러 및 워밍업 단계 수는 모두 서로 상호 작용합니다. 두 개를 고정하고 세 번째를 변경하면 데이터 세트에서 학습 출력이 어떻게 변경되는지에 대한 더 나은 통찰력을 얻을 수 있습니다.
가중치 감소 및 LoRA 드롭아웃 매개변수는 과적합을 제어하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 어댑터가 학습 세트에서 평가 세트로 제대로 일반화되지 않는 경우 이러한 매개변수 값을 늘려보세요.
adam_ 매개변수는 학습 단계 동안 Adam 옵티마이저의 동작 방식에 영향을 미칩니다. 해당 옵티마이저에 대한 자세한 내용은 예를 들어 PyTorch 설명서를 참조하세요.
노출된 다른 매개변수 중 상당수는 PEFT 라이브러리의 동등한 이름의 매개변수와 유사합니다. 해당 매개변수에 대한 자세한 내용은 transformers 설명서를 참조하세요.
데이터 하이퍼파라미터
데이터 하이퍼파라미터 train_nsamples 및 test_nsamples는 각각 학습 및 테스트에 사용할 샘플 수를 제어합니다. 학습 세트에서 더 많은 샘플을 사용하는 것이 일반적으로 좋습니다. 더 많은 테스트 샘플을 사용하면 잡음이 적은 테스트 지표를 얻을 수 있지만 각 평가 실행에는 더 오래 걸립니다.
train_batch_size 및 test_batch_size 매개변수는 각각 학습 및 테스트에 사용할 각 배치 샘플 수를 제어합니다. 테스트 예제를 실행하는 것이 학습 예제를 실행하는 것보다 GPU 메모리를 덜 사용하기 때문에 일반적으로 테스트에 학습보다 더 많은 배치를 사용할 수 있습니다.
train_seqlen 및 test_seqlen 매개변수는 학습 및 테스트 시퀀스의 길이를 제어합니다. 일반적으로 GPU 메모리 한도에 도달할 때까지 길수록 좋습니다. 기본값은 좋은 균형을 제공해야 합니다.
시스템 프롬프트 선택
학습에 사용할 시스템 프롬프트를 선택할 때 잘 작동하는 것으로 확인된 전략은 1~2 문장으로 비교적 간단하게 유지하면서 모델이 원하는 형식으로 출력을 생성하도록 유도하는 것입니다. 또한 학습 및 추론에 대해 약간 다른 시스템 프롬프트를 사용하면 결과가 향상될 수 있음을 발견했습니다.
원하는 출력과 기본 모델 간의 차이가 클수록 시스템 프롬프트가 더 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 젊은 독자를 대상으로 언어를 단순화하는 것과 같이 기본 모델의 스타일만 약간 변경하도록 학습하는 경우 시스템 프롬프트가 전혀 필요하지 않을 수 있습니다.
하지만 원하는 출력에 더 많은 구조가 필요한 경우 시스템 프롬프트를 사용하여 모델이 부분적으로 거기에 도달하도록 하고 싶을 것입니다. 따라서 특정 키가 있는 JSON 테이블이 필요한 경우 시스템 프롬프트의 첫 번째 문장은 모델 응답이 일반 언어로 응답하는 경우 어떻게 보일지 설명할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 두 번째 문장은 JSON 테이블 형식이 어떻게 보여야 하는지 더 구체적으로 지정할 수 있습니다. 학습 시 첫 번째 문장을 사용하고 추론 시 두 문장을 모두 사용하면 원하는 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
매개변수
미세 조정할 수 있는 모든 매개변수 목록이 여기에 첨부됩니다. 워크플로 페이지 UI에 매개변수가 표시되지 않으면 <your_project_path>/<model_name>/lora/lora.yaml에 수동으로 추가하세요.
[
################## Basic config settings ##################
{
"groupId": "data",
"fields": [
{
"name": "system_prompt",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "Optional system prompt. If specified, the system prompt given here will be prepended to each example in the dataset as the system prompt when training the LoRA adapter. When running inference the same (or a very similar) system prompt should be used. Note: if a system prompt is specified in the training data, giving a system prompt here will overwrite the system prompt in the dataset.",
"label": "System prompt"
},
{
"name": "varied_seqlen",
"type": "bool",
"defaultValue": false,
"info": "Varied sequence lengths in the calibration data. If False (default), training examples will be concatenated together until they are finetune_[train/test]_seqlen tokens long. This makes memory usage more consistent and predictable. If True, each individual example will be truncated to finetune_[train/test]_seqlen tokens. This can sometimes give better training performance, but also gives unpredictable memory usage. It can cause `out of memory` errors mid training, if there are long training examples in your dataset.",
"label": "Allow varied sequence length in data"
},
{
"name": "finetune_dataset",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "wikitext2",
"info": "Dataset to finetune on.",
"label": "Dataset name or path"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_nsamples",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 4096,
"info": "Number of samples to load from the train set for finetuning.",
"label": "Number of finetuning samples"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_nsamples",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 128,
"info": "Number of samples to load from the test set for finetuning.",
"label": "Number of test samples"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_batch_size",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 4,
"info": "Batch size for finetuning training.",
"label": "Training batch size"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_batch_size",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 8,
"info": "Batch size for finetuning testing.",
"label": "Test batch size"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_seqlen",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 2048,
"info": "Maximum sequence length for finetuning training. Longer sequences will be truncated.",
"label": "Max training sequence length"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_seqlen",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 2048,
"info": "Maximum sequence length for finetuning testing. Longer sequences will be truncated.",
"label": "Max test sequence length"
}
]
},
{
"groupId": "finetuning",
"fields": [
{
"name": "early_stopping_patience",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 5,
"info": "Number of evaluations with no improvement after which training will be stopped.",
"label": "Early stopping patience"
},
{
"name": "epochs",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1,
"info": "Number of total epochs to run.",
"label": "Epochs"
},
{
"name": "eval_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 64,
"info": "Number of training steps to perform before each evaluation.",
"label": "Steps between evaluations"
},
{
"name": "save_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 64,
"info": "Number of steps after which to save model checkpoint. This _must_ be a multiple of the number of steps between evaluations.",
"label": "Steps between checkpoints"
},
{
"name": "learning_rate",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.0002,
"info": "Learning rate for training.",
"label": "Learning rate"
},
{
"name": "lr_scheduler_type",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "linear",
"info": "Type of learning rate scheduler.",
"label": "Learning rate scheduler",
"optionValues": [
"linear",
"linear_with_warmup",
"cosine",
"cosine_with_warmup"
]
},
{
"name": "num_warmup_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 400,
"info": "Number of warmup steps for learning rate scheduler. Only relevant for a _with_warmup scheduler.",
"label": "Scheduler warmup steps (if supported)"
}
]
}
################## Advanced config settings ##################
{
"groupId": "advanced",
"fields": [
{
"name": "seed",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 42,
"info": "Seed for sampling the data.",
"label": "Random seed"
},
{
"name": "evaluation_strategy",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "steps",
"info": "Evaluation strategy to use.",
"label": "Evaluation strategy",
"optionValues": [
"steps",
"epoch",
"no"
]
},
{
"name": "lora_dropout",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.1,
"info": "Dropout rate for LoRA.",
"label": "LoRA dropout"
},
{
"name": "adam_beta1",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.9,
"info": "Beta1 hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam beta 1"
},
{
"name": "adam_beta2",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.95,
"info": "Beta2 hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam beta 2"
},
{
"name": "adam_epsilon",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1e-08,
"info": "Epsilon hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam epsilon"
},
{
"name": "num_training_steps",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "The number of training steps there will be. If not set (recommended), this will be calculated internally.",
"label": "Number of training steps"
},
{
"name": "gradient_accumulation_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 1,
"info": "Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
"label": "gradient accumulation steps"
},
{
"name": "eval_accumulation_steps",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "Number of predictions steps to accumulate before moving the tensors to the CPU.",
"label": "eval accumulation steps"
},
{
"name": "eval_delay",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": 0,
"info": "Number of epochs or steps to wait for before the first evaluation can be performed, depending on the eval_strategy.",
"label": "eval delay"
},
{
"name": "weight_decay",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.0,
"info": "Weight decay for AdamW if we apply some.",
"label": "weight decay"
},
{
"name": "max_grad_norm",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1.0,
"info": "Max gradient norm.",
"label": "max grad norm"
},
{
"name": "gradient_checkpointing",
"type": "bool",
"defaultValue": false,
"info": "If True, use gradient checkpointing to save memory at the expense of slower backward pass.",
"label": "gradient checkpointing"
}
]
}
]
Azure 구독 및 리소스 그룹 수정
이전에 설정한 Azure 구독 및 리소스 그룹을 수정하려면 <your_project_path>/model_lab.workspace.provision.config 파일을 업데이트하거나 제거할 수 있습니다.
Phi Silica LoRA 어댑터를 사용한 추론
Phi Silica API는 제한 액세스 기능( LimitedAccessFeatures 클래스 참조)의 일부입니다. 자세한 정보 또는 잠금 해제 토큰 요청은 LAF 액세스 토큰 요청 양식을 사용하세요.
Phi Silica LoRA 어댑터를 사용한 추론은 현재 ARM 프로세서가 있는 Copilot+ PC에서만 지원됩니다.
Windows AI API를 사용하여 추론: LoRA 어댑터를 사용하는 Phi Silica